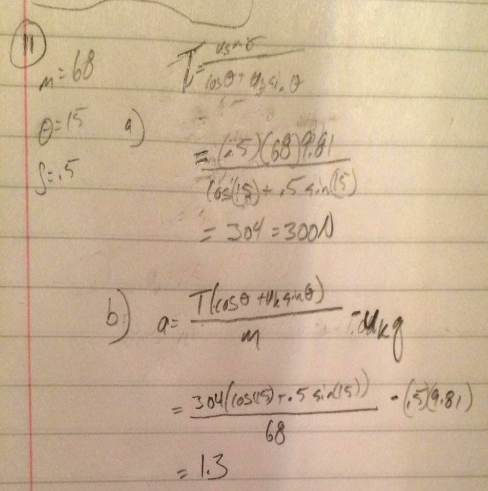A box is dragged across a floor by a rope which makes an angel 45 degree with the horizontal the tension in the rope is 100n while the box is dragged 10m the work done is.
A box is dragged across a floor.
The rope makes an angle of 30 with the horizontal and has a tension of 5 n.
A box is being dragged across the floor at a constant speed by a rope pulling horizontally on it.
A box is dragged a distance d across a floor by a force which makes an angle with the horizontal as in fig.
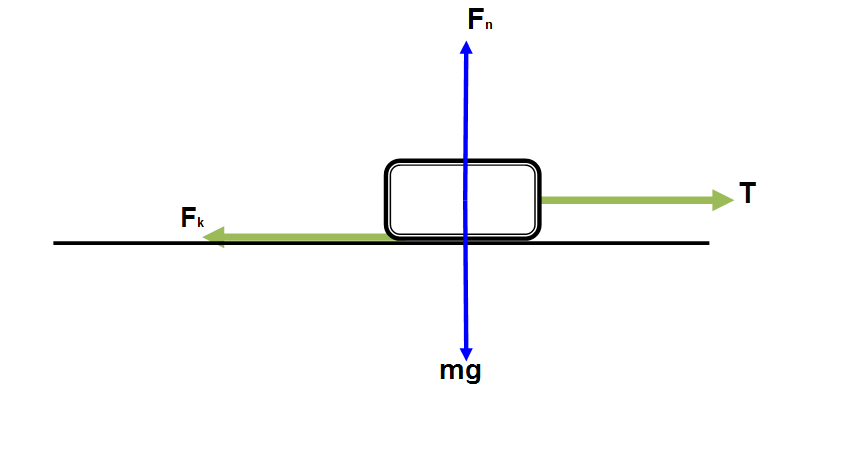
Part a identify all the forces acting on the box.
D first increases then decreases.
If the magnitude of is held constant but the angle is increased the work done by a remains the same.
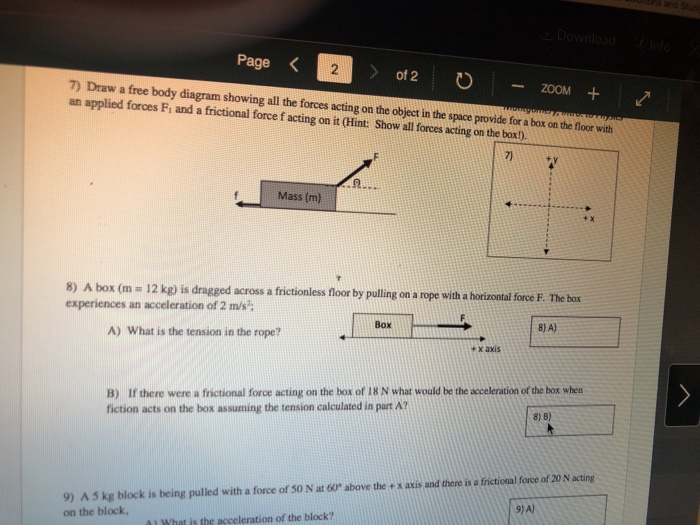
Which of the following would be closest to the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the floor if a 250 newton force on the rope is required to move the crate at a constant speed of 20 m s as shown in the diagram.
The box dragged at a distance of 10 m.
It is given that a box is dragged across a floor by a rope which makes an angle of 45 with the horizontal.
Part b draw a free body diagram of the box.
A box with mass m is dragged across a level floor having a coefficient of kinetic friction µk by a rope that is pulled upward with an angle θ above the horizontal with a force of magnitude f a in terms of m µk θ and g obtain an expression for the magnitude of force required to move the box with constant speed.
Tension in the rope t 100 n.
A box with mass m is dragged across a level floor having a coefficient of kinetic friction μk by a rope that is pulled upward at an angle above the horizontal with a force of magnitude f.
Check all that apply.
Friction is not negligible.
G m mu k for μk and theta for θ.
Mathematically it can be written as.
We know that the work done is equal to the product of force displacement and the angle between them.
Kinetic friction force f k tension t weight w normal force n thrust f thrust.
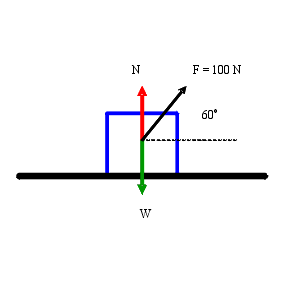
A box with a mass of 50 kg is dragged across the floor by a rope which makes an angle of 30º with the horizontal.